What is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy refers to the spending and taxation decisions a government makes to influence the nation’s economic performance.

Fiscal policy refers to the spending and taxation decisions a government makes to influence the nation’s economic performance. Fiscal policy works in tandem with monetary policy, which is where a central bank or monetary authority controls the interest rate, money supply and exchange rate to influence economic outcomes.
Fiscal policy planning requires a careful balance between public spending and taxation to maintain a sustainable level of economic productivity. A high tax rate to fund large spending programs will disincentive workers to work more and corporations to invest locally. A low tax rate will encourage workers to work more and corporations to invest more. However, it may not raise enough tax revenue to cover spending programs that provide the people with a decent standard of living. More often than not, a government has to decide on how big the public sector should be and how to generate the necessary tax revenue to fund their spending programs without hurting economic competitiveness.
Fiscal policy is also used to smooth out the economic cycles. For example, when the global economy was hit by a large exogenous shock like the recent Covid-19 pandemic, governments all over the world increased their expenditure through larger transfer payments to households and higher healthcare expenditure. With the pandemic all but over, the global economy is now facing elevated levels of inflation with unemployment rates at decade low. To help keep inflation in check and to prevent the economy from overheating, governments are now reducing their spending and raising taxes to cover for the huge budget deficits incurred during the pandemic. Thus, fiscal policy is useful in managing aggregate demand.
Fiscal policy is also used to manage the economy’s long-run aggregate supply. Governments do hand out incentives to the private sector to invest in infrastructure, education, production capacity and buildings to boost the nation’s potential economic output. Ensuring that the future aggregate demand of an economy will be matched by the aggregate supply will help to ensure that inflation will remain low in the long run.
What does Fiscal Policy affect?
Fiscal policy affects different groups of society at different levels, depending on the government’s policy goals. For instance, a policy implementing a tax cut may only impact taxpayers within a specific income range, rather than all taxpayers. Likewise, a change in spending policy may only impact certain groups and have no impact on others..
For example, spending taxpayers’ funds on public infrastructure such as a bridge can provide employment to a large group of construction workers, with a broad range of skills. On the other hand, using public spending on the construction of a fighter jet or nuclear submarine only provides employment to a select group of experts with specialised skills.
Also, the fiscal policies implemented by the government can also impact financial markets at a wider level because of how traders react to these changes. It is also important to note how small changes in the fiscal policy can have a longstanding effect on the economic growth of a country, such as how a small tax cut handed out today can build up and create large fiscal deficits in the future.
Fiscal Policy vs Monetary Policy, Which is Better?
Fiscal policy refers to how governments choose to allocate their spending and taxes to impact the nation’s economy. Monetary policy allows a central bank to exert its influence over the supply of money, interest rate and exchange rate of a particular country. Neither fiscal policy, nor monetary policy is necessarily better than the other. However, both policies are regarded as complementary and need to be implemented in tandem to help steer the economy towards sustainable growth.
Singapore Fiscal Policy
Singapore’s Fiscal Policy is constructed with the goal of promoting economic growth, maintaining economic stability and social equity. Public spending is allocated to the provision of public goods and investment in projects that spur economic growth. This allows for economic success in both the present and the future. The following diagram shows the changes in Singapore’s public spending over the past 10 years.
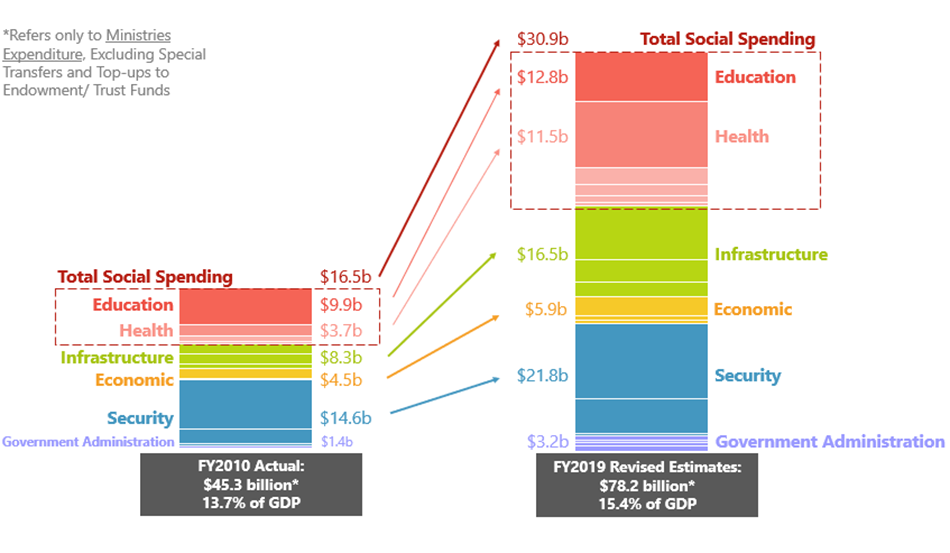
Singapore’s Fiscal Policy takes on a long-term approach, with prioritisation of spending on key economic drivers of the future. For example, Singapore’s policies aim to target growing issues that will have a significant impact on society in the years to come, such as increased spending on aged care due to the aging population and spending on sustainability because of the threat of climate change.
Read also: ESG & Green Buildings: Should They Be an Investment Focus?
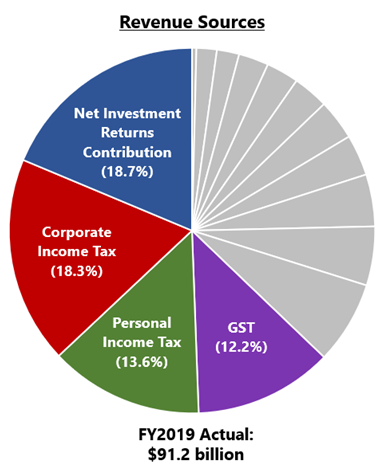
Singapore’s Fiscal Policy also consists of diversification of revenue across multiple streams to ensure economic stability and success in the long run. This allows for fair and equitable contributions and returns across different generations of Singaporeans.
Singapore’s Fiscal Policy continues to include expenditure on development projects which accelerate innovation across critical upcoming sectors, keeping up with digitalisation and raising the overall standard of living nationwide. These policies also encourage cooperation between businesses and social sectors to encourage collective responsibility throughout all sectors of society.
Singapore’s taxation system also follows the same values of equity and fairness, ensuring that the taxes and benefits are equitably distributed, given the income levels of different households. Singapore’s Fiscal Policy extends beyond their economic goals to encourage social mobility, providing equal opportunities to citizens, made possible by spending on key public sectors such as education.
About RealVantage
RealVantage is a leading real estate co-investment platform, licensed and regulated by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), that allows our investors to diversify across markets, overseas properties, sectors and investment strategies.
The team at RealVantage are highly qualified professionals who brings about a multi-disciplinary vision and approach in their respective fields towards business development, management, and client satisfaction. The team is led by distinguished Board of Advisors and advisory committee who provide cross-functional and multi-disciplinary expertise to the RealVantage team ranging from real estate, corporate finance, technology, venture capital, and startups growth. The team's philosophy, core values, and technological edge help clients build a diversified and high-performing real estate investment portfolio.
Get in touch with RealVantage today to see how they can help you in your real estate investment journey.
Disclaimer: The information and/or documents contained in this article does not constitute financial advice and is meant for educational purposes. Please consult your financial advisor, accountant, and/or attorney before proceeding with any financial/real estate investments.
